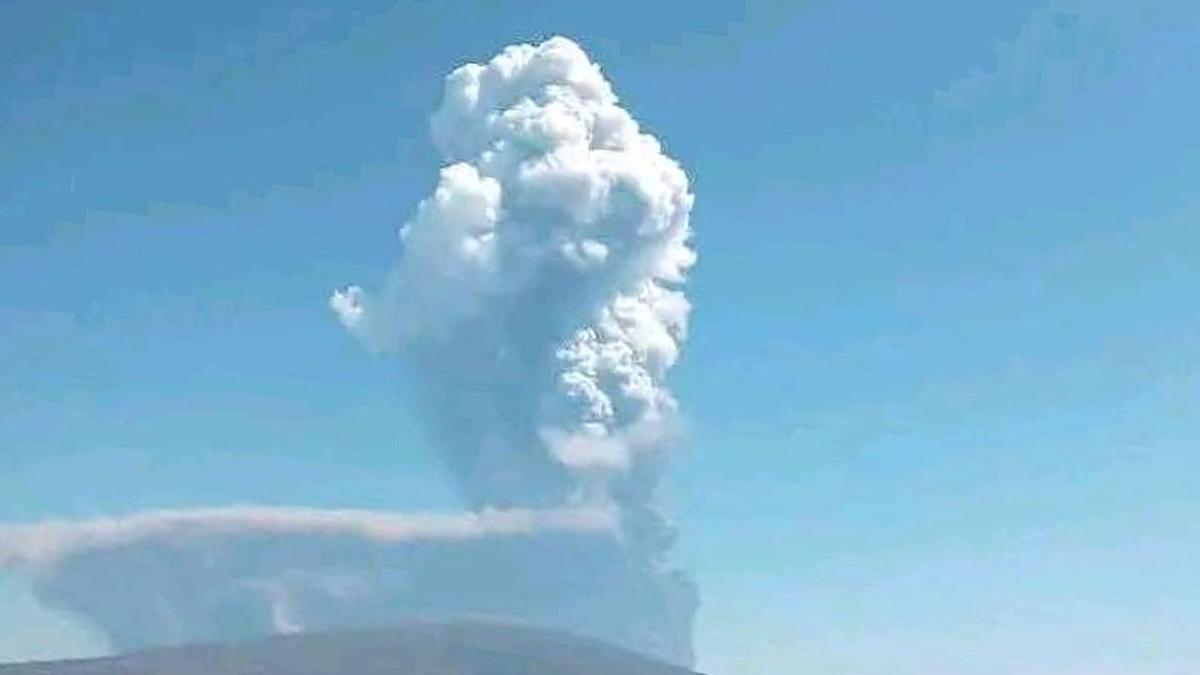
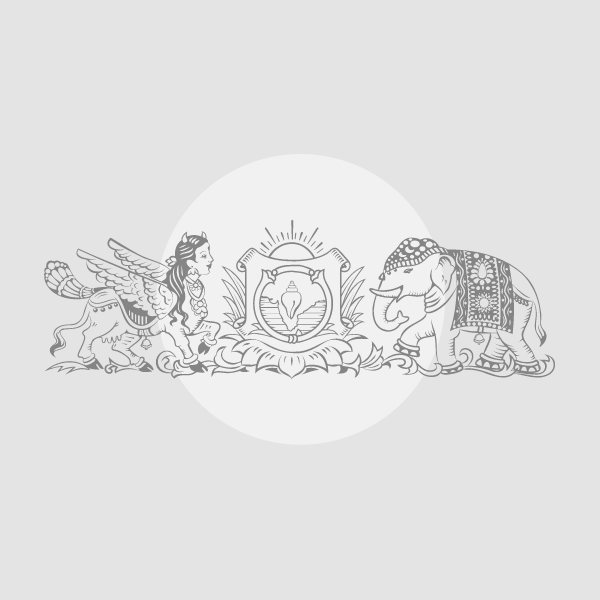
In this photo released by the Afar Government Communication Bureau, ash billows from an eruption of the long-dormant Hayli Gubbi Volcano in Ethiopia’s Afar region on November 23, 2025.
| Photo Credit: AP
Multiple flights to and from Hyderabad were cancelled on Tuesday (November 25, 2025) after aviation authorities warned of possible ash cloud movement towards western India following the eruption of the Hayli Gubbi volcano in Ethiopia. The disruption prompted Rajiv Gandhi International Airport (RGIA) to issue a passenger advisory.
List of flights cancelled
Among the cancelled services were Air India’s AI 2204 from Dubai to Hyderabad, AI 2466 from Hyderabad to Delhi, and AI 2444/2445 operating on the Mumbai–Hyderabad–Mumbai route. An IndiGo flight, 6E 1316 from Doha to Hyderabad was also cancelled. Officials noted that while airport operations in Hyderabad remain normal, further schedule changes cannot be ruled out as conditions continue to evolve.
In its advisory, the airport stated that some flights may experience delays or cancellations depending on evolving conditions. Travellers were asked to check the latest flight status with their respective airlines before proceeding to the airport.
Meanwhile, airlines have begun issuing statements on the disruptions. A spokesperson for Akasa Air said the carrier had cancelled its services to and from Jeddah, Kuwait and Abu Dhabi scheduled for November 24 and 25. Passengers have been given the option of a full refund for their existing bookings or the choice to rebook on an alternative flight within the next seven days at no additional charge, the spokesperson added.
Why is volcanic ash a threat to aircraft engines?
The DGCA had earlier issued advisories asking airlines to avoid flying through affected altitudes and regions in the interest of safety, as volcanic ash poses a serious risk to aircraft engines. The ash contains abrasive, glass-like particles that melt at high temperatures, and when ingested by an engine, they can liquefy, solidify again, and form a glassy coating on turbine blades, potentially causing engine failure.
Published – November 25, 2025 11:45 am IST