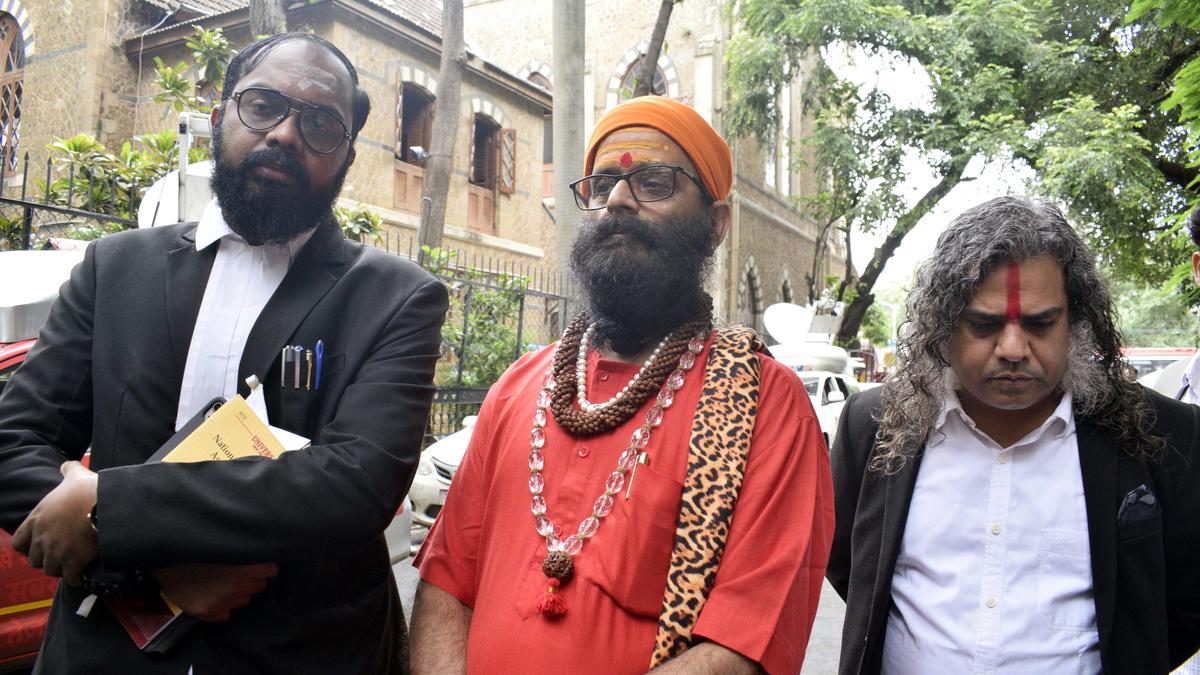
A Special National Investigation Agency (NIA) Court on Thursday (July 31, 2025) acquitted all seven accused in the 2008 Malegaon bomb blast case, including Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) leader and former Member of Parliament (MP) Pragya Singh Thakur and serving Army Lieutenant Colonel Prasad Purohit.
In a detailed 1,036-page judgment that was delivered on July 31 and made available on August 1 evening, Special Judge A.K. Lahoti observed that although the occurrence of the bomb blast was indisputable, the prosecution had failed to produce credible and admissible evidence establishing the accused’s involvement in the crime.

“I am fully aware of the degree of agony, frustration, and trauma caused to society at large and, more particularly, to the families of the victims by the fact that a heinous crime of this nature has gone unpunished. However, the law does not permit courts to convict an accused solely on the basis of moral conviction or suspicion. No doubt, terrorism has no religion because no religion in the world preaches violence. The court of law is not supposed to proceed on popular or predominant public perceptions about the matter,” the Judge underscored. However, he directed the State Government to pay compensation of ₹2 lakh to the families of the deceased and ₹50,000 to those injured in the blast.
Editorial | By evidence alone: on the 2008 Malegaon blast trial
What was the Malegaon blast case?
On September 29, 2008, during the holy month of Ramzan, a powerful bomb blast ripped through Malegaon, a communally sensitive town in Maharashtra. Around 9:35 p.m., an explosive device concealed in an LML Freedom motorcycle with a fake number plate (MH-15-P-4572) detonated near Shakeel Goods Transport Company, between Anjuman Chowk and Bhiku Chowk. The explosion killed six people, injured 95 others, and caused significant damage to surrounding property. An FIR was promptly registered, and the investigation was initially undertaken by the Nashik Rural Police and Mumbai’s Anti-Terrorism Squad (ATS), then headed by Hemant Karkare, who was later killed in the 26/11 Mumbai attacks. In 2011, the case was transferred to the NIA as part of a wider probe into alleged Hindutva-linked terror cases.

Of the 14 individuals arrested in connection with the blast, charges against seven were eventually dropped. The remaining seven, Pragya Singh Thakur, Colonel Prasad Shrikant Purohit, Ramesh Upadhyay, Sameer Kulkarni, Ajay Rahirkar, Sudhakar Dwivedi, and Sudhakar Chaturvedi, were put on trial. They were prosecuted for murder and criminal conspiracy under various provisions of the Indian Penal Code, 1860, along with charges under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), 1967, and the Explosive Substances Act, 1908.
According to the ATS, conspiracy meetings had taken place across various locations allegedly under Ms. Thakur’s leadership. The agency also claimed that the two absconding accused, Ramji Kalsangra and Sandeep Dange, had assembled the explosive device and placed it in the boot of a motorcycle registered to Ms. Thakur. However, several witnesses, including serving Army officers, later retracted their statements in court, alleging that their earlier testimonies had been coerced. Many of the accused also claimed that their confessions were extracted under torture. The NIA appeared to accept parts of these allegations in its final chargesheet, which the defence used to bolster its case.

The case also attracted widespread attention following the resignation of NIA special public prosecutor Rohini Salian, who alleged that she had been instructed to “go soft” on the accused and that the agency was deliberately weakening the case against the so-called “Hindu terror” network. After her departure, special public prosecutor Avinash Rasal took over and conducted the trial to its conclusion.
Why were the accused acquitted by the court?
Here are some of the key findings:
Thakur was not in ‘conscious possession’ of motorcycle
The court held that Ms. Thakur was not in “conscious possession” of the LML Freedom motorcycle in which the explosive device was allegedly planted. Citing her renunciation of the material world at least two years before the blast, Judge Lahoti observed, “Prosecution had not led any evidence on record to show that she was in conscious possession of the said motorcycle even after renouncement of the material world. Nobody has seen her with the said motorcycle, or it was with her at Jabalpur Aashram even after taking the Sanyas.”
The Judge further observed that there was neither eyewitness testimony nor circumstantial evidence to suggest that Ms. Thakur had handed over the motorcycle to the co-accused or was involved in assembling the explosive device. Instead, he noted that the explosive could have been hung, placed, or kept near the motorcycle, rather than fitted inside it. “Mere, blast on the site and damaged condition of the motorcycle are not conclusive proof of fitting explosives inside the dikki, i.e., beneath the seat of said motorcycle,” the Judge observed, adding that expert testimony did not rule out the possibility of the device being attached externally or placed nearby.
As for allegations of torture by the ATS, the court noted that Ms. Thakur had not raised any such complaint when she was produced before a magistrate on October 24, 2008, following her arrest. Citing an earlier Supreme Court order, the Judge pointed out that she neither made any allegations of ill-treatment at the time nor challenged the magistrate’s remand order.
No official sanction for Purohit’s association with Abhinav Bharat
The ATS alleged that the explosive used in the blast was RDX, claiming it had been procured by Colonel Purohit during his posting in Jammu & Kashmir. However, the court found no evidence establishing the source of the explosive or how it was procured or transported. It also noted the absence of any proof regarding who had parked the motorcycle at the blast site or when, particularly since the area had been cordoned off for Ramzan.
However, Judge Lahoti rejected Mr. Purohit’s claim that his association with fringe organisations like Abhinav Bharat was part of his official duties as an intelligence officer. He noted that documentary evidence clearly established Mr. Purohit’s role as a trustee of the Abhinav Bharat Trust. However, there was no material on record to suggest that his superiors had authorised him to join the trust or to collect and utilise its funds. “As per the ethos of the Military Intelligence, the commanding officer or the Discipline & Vigilance Branch used to protect the interests of officers and sources. But after the arrest of A-9 (Mr. Purohit), no steps were taken to protect their officer. If he had really discharged the duty under the colour of his office, there would have been protection for him,” the Judge reasoned.
Absence of forensic evidence
Judge Lahoti observed that the forensic expert who examined the motorcycle, on which the explosive device was allegedly planted, had admitted that it was merely his “guesswork” that led him to conclude the bomb was placed in the vehicle’s boot. No scientific test had been conducted to verify the placement of the explosive. Accordingly, the Judge held that in the absence of any primary forensic analysis, the expert’s testimony failed to inspire confidence.
“The present matter is [a] serious case of bomb-blast. In such a case, mere guess work is not enough. Neither it is expected from expert when he is specifically called on the spot to collect the articles, to assist and to guide the Investigating Agency by carrying out some scientific tests. In such situation, there must be some scientific test to be carried out by an expert on the spot to arrive at certain conclusion,” the Judge emphasised.
Procedural lapses in the invocation of MCOCA and UAPA
The ATS, which initially investigated the blast, based its case primarily on the accused having participated in conspiracy meetings related to the planning and execution of the attack. Its key evidence comprised confessional statements recorded under the Maharashtra Control of Organised Crime Act (MCOCA), 1999. However, these confessions were rendered inadmissible after MCOCA was dropped from the case in 2016, when the NIA took over the investigation and flagged procedural lapses in the Act’s invocation.

The court concurred, noting that the sanction to invoke MCOCA had been granted without “application of judicial mind.” A similar procedural lapse was found in the invocation of the UAPA. Judge Lahoti noted that the then Additional Chief Secretary of the Home Department, Mumbai, Chitkala Zutshi, had failed to consult the investigating officer before granting sanction under the UAPA. As a result, the statutory presumptions under the Act, such as the reverse burden of proof, could not be invoked against the accused, the court held.
No merit in claim that ATS directed arrest of RSS chief
The court rejected the claim made by former ATS officer Mehboob Mujawar that he had been instructed to arrest RSS chief Mr. Mohan Bhagwat in connection with the case. Judge Lahoti found no merit in the argument advanced by the lawyer for the accused, Mr. Sudhakar Dhar Dwivedi, who had relied on Mr. Mujawar’s statements before a Solapur court. Mr. Mujawar had alleged that senior ATS officers directed him to arrest Mr. Bhagwat to frame the case as one of “saffron terror,” but said he refused, having found no evidence linking Mr. Bhagwat to the alleged crime.
However, the Judge relied on the testimony of Mr. Mohan Kulkarni, the then chief investigating officer, who stated that Mr. Mujawar was only tasked with tracing the absconding accused, Mr. Ramji Kalsangra and Mr. Sandeep Dange, and was never instructed to arrest any RSS leader. The court also noted that Mr. Mujawar was neither listed nor examined as a witness by either side. Accordingly, it concluded that the statements submitted were part of Mr. Mujawar’s defence in another case and held no evidentiary value in the present trial.
What happens next?
Advocate Shahid Nadeem, representing Nisar Ahmed Haji Sayyed Bilal, who lost his son in the blast, told the media that the case reflected “significant failures” on the part of the NIA. He added that the victims’ families intend to explore legal remedies by filing an independent appeal in the Bombay High Court after reviewing the full judgment.
Meanwhile, political pressure is mounting on the Maharashtra Government to file its own appeal, as it did following the acquittals in the 2006 Mumbai train blasts case. Twelve Muslim men were acquitted after spending 19 years in prison, with the High Court issuing scathing observations on the use of torture during the investigation. The State had moved the Supreme Court the very next day, prompting the apex court to clarify that the High Court’s observations could not serve as precedent in other similar cases.
In the present case, however, Special Public Prosecutor Avinash Rasal, appearing for the NIA, said a decision on whether to file an appeal would be made only after a detailed study of the judgment.