A few weeks back, India’s Finance Ministry declared the Indian economy to be in a “Goldilocks situation” — a rare alignment of moderate growth, subdued inflation and supportive monetary conditions. Analysts too, taking a narrow, quarterly view of the Indian economy conceded, marking this as a “mini-Goldilocks moment” for its macroeconomic position, spurred by 7.6% GDP growth, peaking interest rates and stable corporate earnings. A few other macroeconomic observers pointed out that India exiting FY2024 as a $3.6 trillion economy with an underlying growth of over 7.6% projects a buoyant macroeconomic backdrop for 2025.
Yet beneath the veneer and hyper-optimistic outlook lies a more complex reality for India’s macroeconomic position. More astute observers of the Indian economy with historical data, question this so-called golden equilibrium which disguises underlying structural imbalances.
Inflation and stagnant wage growth
A closer look at Chart 1 reveals a nuanced story behind headline price stability. While the Consumer Price Index (CPI) indeed showed a commendable deceleration, falling from 4.8% in May 2024 to 2.82% by May 2025, hinting at inflation within the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) comfort zone, the path to this point and the underlying dynamics, warrant significant scrutiny.
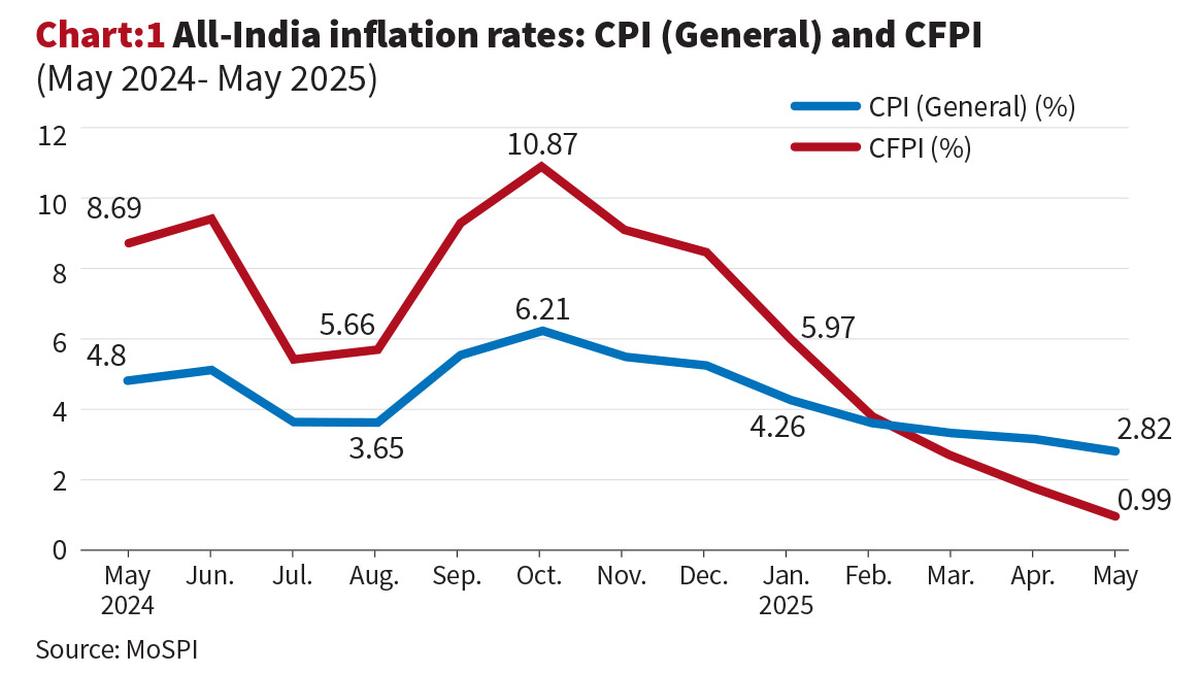
Throughout much of 2024, the Consumer Food Price Index (CFPI) consistently ran significantly higher than general inflation. For instance, in October 2024, when CPI (General) peaked at 6.21%, CFPI surged to an alarming 10.87%. Even in August 2024, with CPI at 3.65%, CFPI stood at 5.66%. This persistent divergence is critical because food accounts for nearly half of the consumption basket of an average Indian household, particularly within lower-income groups. High and volatile food inflation, driven by factors like unseasonal rains, supply chain disruptions and global commodity price fluctuations, severely erodes the purchasing power of the common citizen.
Economists like Dr. Pronab Sen have argued that policymakers such as the RBI should focus on core inflation rather than headline CPI inflation, because core inflation excludes volatile food and fuel prices and better reflects the sustained burden of price increases across essentials like housing, education, transport, and personal care.
For an average family, the meaning of 10% food inflation is a direct and painful cut in real income, forcing them to either compromise on dietary quality, incur debt or drastically reduce other essential expenditures. The eventual dip in CFPI to 0.99% by May 2025, while welcome, must be viewed in the context of the preceding periods of severe pressure. The volatility itself creates uncertainty and hinders household budgeting and savings, directly countering the stability implied by a “Goldilocks” environment.
This inflationary pressure on essentials directly impacts the everyday reality captured in Chart 2 which delivers one of the most compelling arguments against the “Goldilocks” perception.
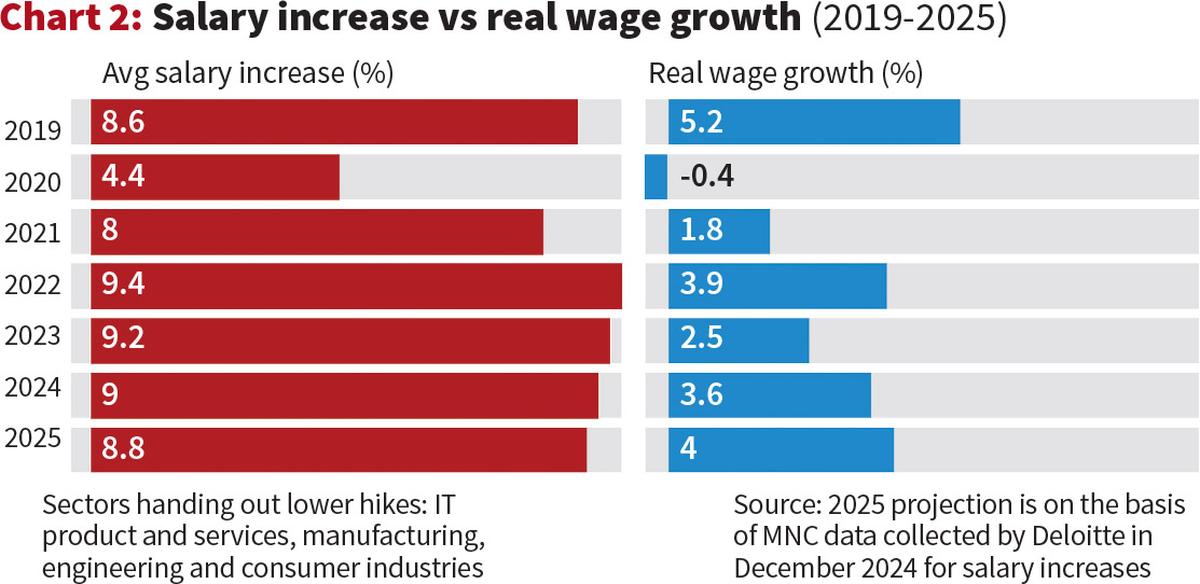
This data powerfully illustrates the chasm between nominal salary hikes and the actual improvement in purchasing power. For instance, in 2023, while the average salary increase was a respectable 9.2%, the real wage growth stood at a mere 2.5%. More critically, in 2020, real wage growth turned negative, registering -0.4%, even as nominal salaries saw a 4.4% rise. Even the 2025 projection of 4% real wage growth against an 8.8% average salary increase indicates that half of the nominal gain is still being eroded by inflation. This numerical gap translates into a tangible daily struggle. A 9% salary hike sounds promising, but if inflation is 7%, their actual ability to buy goods and services only increases by 2%.
This “silent squeeze” diminishes household savings, forces families to cut back on discretionary spending, and can lead to increased reliance on debt, particularly for those in sectors like IT product and services, manufacturing, engineering, and consumer industries, which usually hand out lower hikes.
Income inequality
The International Labour Organization (ILO) and various labour economists have consistently pointed out challenges vis-à-vis job quality and stagnant real wages in many emerging economies, including India. Without substantial and sustained growth in real wages, the consumption demand, which is a critical driver for the Indian economy, remains constrained, undermining the foundations of a truly buoyant and broad-based economic recovery.
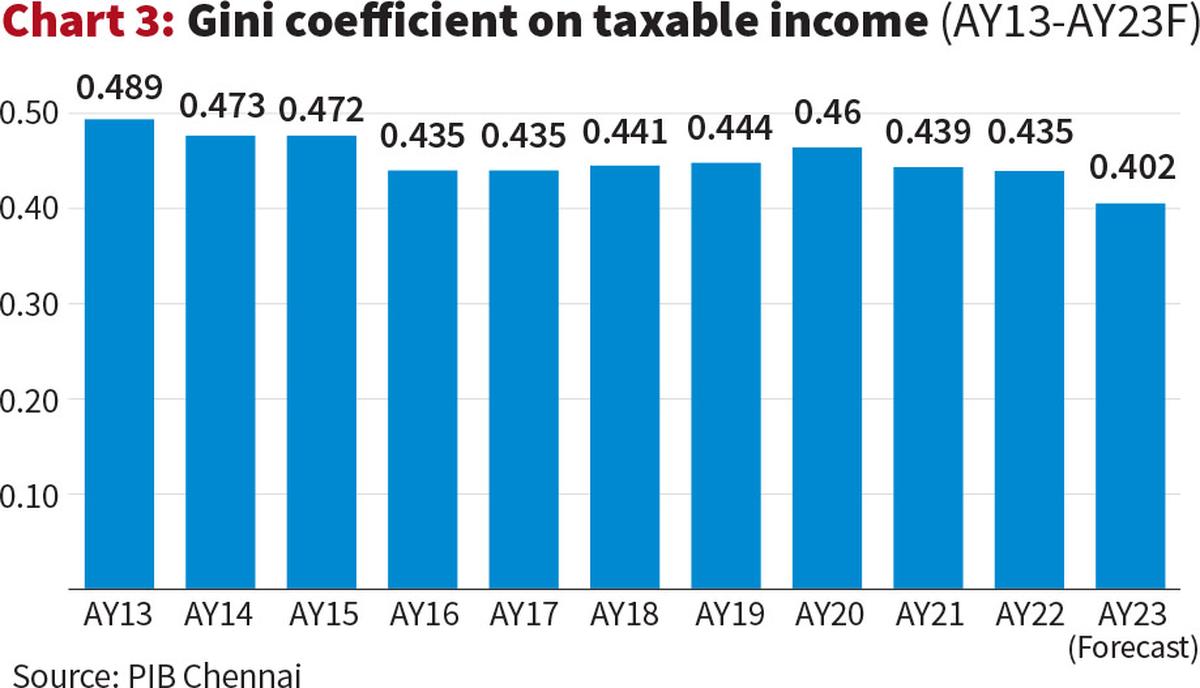
This unevenness in economic gains also finds reflection in Chart 3, which offers a glimpse into income distribution. The Gini coefficient, a measure of inequality, shows fluctuations over the decade, starting at a high of 0.489 in AY13, dipping to 0.435 in AY16, and forecasted at 0.402 for AY23. While a declining Gini coefficient on taxable income might suggest some improvement, it is crucial to recognise the limitations.
Taxable income primarily captures the formal sector and those above a certain income threshold, potentially missing the vast informal sector and the broader distribution of wealth. A recent essay by ORF authors Garima Nain and Ria Kasliwal describe India’s post-pandemic economy as a multi-speed or K-shaped recovery, where certain segments, particularly the affluent and those in specific industries, thrive, while others lag.
While the number of billionaires in India has surged, real wages for many at the lower end of the income spectrum have remained the same. This persistent inequality can undermine social cohesion, limit access to quality education and healthcare for a large segment of the population, and ultimately stifle long-term inclusive growth. When a significant portion of the population feels left behind, despite robust GDP numbers, the notion of a universally beneficial “Goldilocks” state becomes deeply questionable.
Adding to these domestic pressures, Chart 4 showcases the government’s fiscal position and its trajectory. While there’s a clear commitment to fiscal consolidation, with the fiscal deficit projected to decline from 6.4% in 2022-23 to 4.4% in 2025-26 (budget estimate), and the revenue deficit decreasing from 4% to 1.5% over the same period, the absolute levels of these deficits remain substantial.
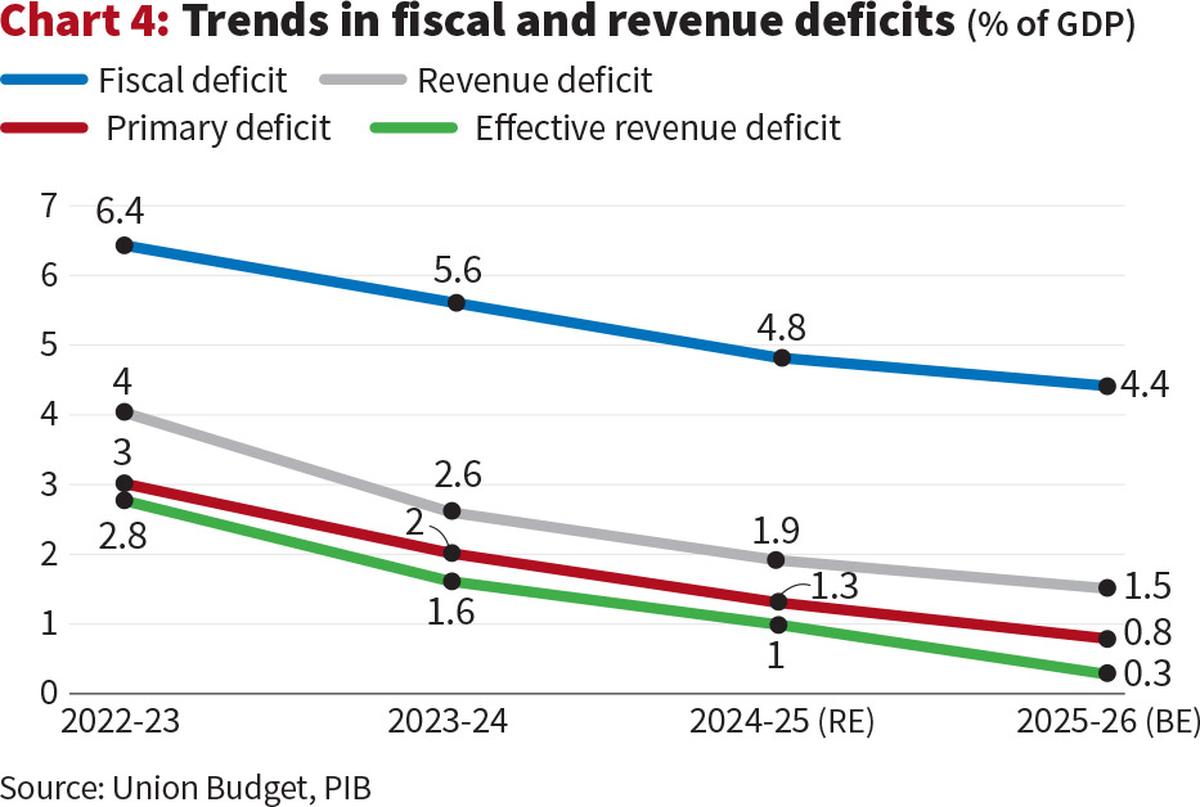
The primary deficit, which indicates the current year’s borrowing excluding interest payments on past debt, is also projected to fall from 3% to 0.8%. However, for a developing economy like India, sustained high deficits can pose several macroeconomic challenges. They necessitate significant government borrowing, which can potentially crowd out private investment by increasing demand for funds and putting upward pressure on interest rates. This could deter private businesses from investing and expanding, thus limiting job creation and overall economic growth.
Furthermore, a high public debt-to-GDP ratio (which stood at around 81% for the general government in 2022-23, significantly above the fiscal responsibility and budget management Act target of 60%) implies a substantial portion of future revenues will be diverted to servicing this debt. For the average citizen, this translates into reduced fiscal space for critical public spending on social sectors like education, healthcare, and infrastructure, or potentially higher taxes in the future to manage the debt burden.
Complicating the goldilocks narrative
Taken together, these critical indicators, volatile food inflation eroding purchasing power, persistent income disparities despite growth, stagnant real wages for the majority, and a tight fiscal space, paint a picture far more complex than the harmonious “Goldilocks” narrative suggests. The so-called macro sweet spot is not universally experienced, and therefore, its underlying fragilities are becoming increasingly apparent. The socio-economic realities on the ground, consistently analysed by a broad spectrum of economists, reveal that the journey towards inclusive and sustainable prosperity for all Indians remains an uphill climb.
Indeed, for those willing to look beyond the headlines and delve into the granular data, the myth of the macro sweet spot is cracking open.
The allure of a “Goldilocks” economy, while comforting, risks obscuring the lived realities of millions. True economic equilibrium transcends mere GDP numbers or headline inflation targets; it’s fundamentally about how these aggregate statistics translate into tangible improvements in daily lives.
When real wages stagnate against rising costs, when growth disproportionately benefits a select few, and when the government operates under significant fiscal constraints, the promise of a “just right” economy rings hollow for the common household. India’s true economic strength will not be defined by fleeting perceptions of balance, but by its capacity to foster genuinely inclusive growth, bolster real incomes, and build robust fiscal resilience for all its citizens. It is in addressing these profound challenges, rather than embracing a superficial sweet spot, that India’s sustainable economic future lies.
Deepanshu Mohan is Professor of Economics and Dean, O.P. Jindal Global University (JGU) and Visiting Professor, London School of Economics (LSE). Ankur Singh contributed to this column.























