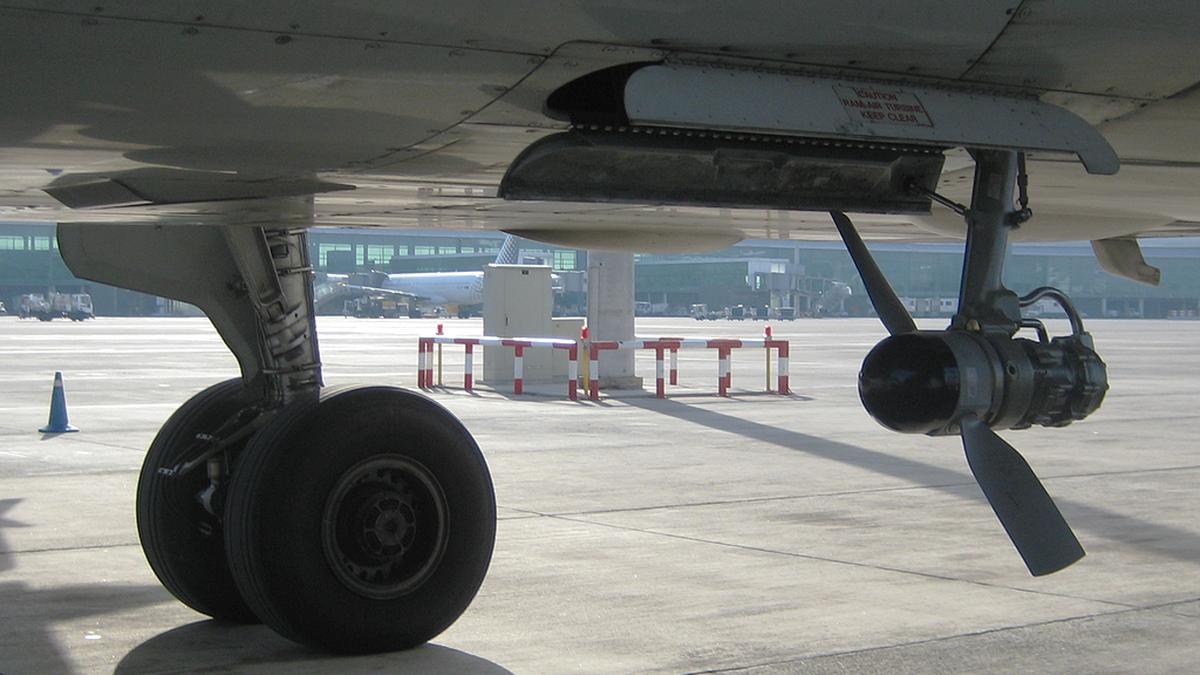
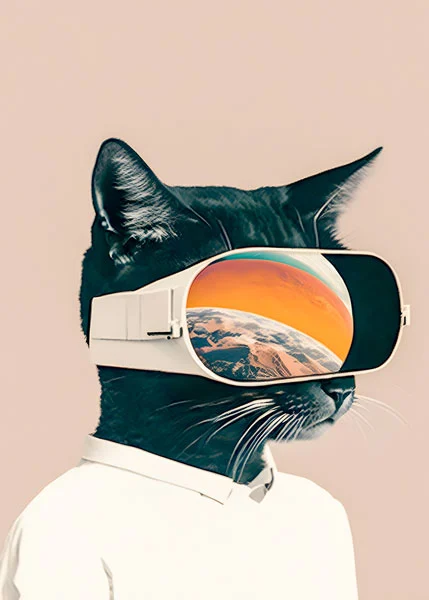
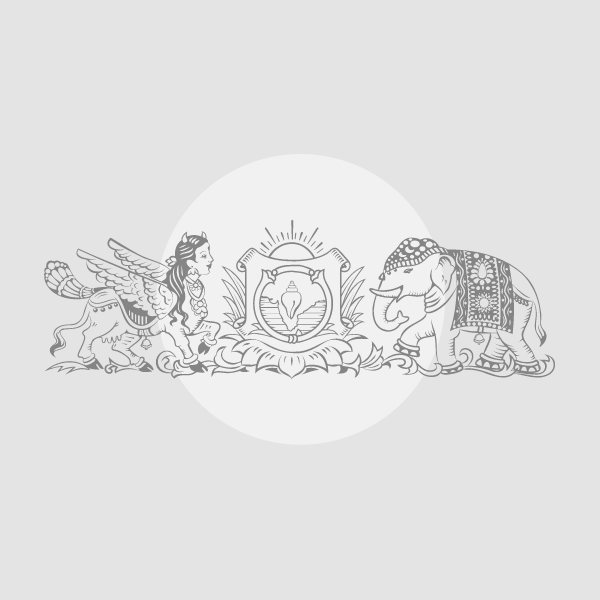
A ram air turbine deployed in an Airbus A320.
| Photo Credit: Curimedia (CC BY)
A preliminary investigation by the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau has said the Air India Boeing 787-8 crash near Ahmedabad on June 12 followed fuel to the vehicle’s two engines being cut off.
The engines on the 787-8 are the main source of power and the aircraft model is famed for being highly electrified.
According to CCTV footage from the airport, the vehicle subsequently deployed its ram air turbine (RAT) in a bid to have some power so the flight could be steered to safety.
Air India Ahmedabad plane crash victims | Tales of grief and loss
A ram air turbine (RAT) is a small device found on many airplanes. It is installed with the goal of providing emergency power if the plane’s main systems fail.
The RAT is usually tucked away inside the plane, often in the wing or fuselage, and does nothing while the engines and main systems are working.
However, if the plane loses its principal source of power, such as due to engine failure, the RAT pops out to face the airstream. This can happen automatically or manually.
As the main engines have already left the plane with a momentum through the air, air rushing past the RAT causes its blades to spin.
The spinning RAT turns a generator or a hydraulic pump. This creates just enough electricity or hydraulic pressure to keep the most important systems running, including flight controls, basic instruments, and radio and communication equipment.
The faster the plane is already moving, the more power the RAT can generate. Even so, the RAT does not provide full power, only enough to keep the plane safe until it can land.
Most RATs deploy automatically if there is a major power failure, but pilots can also deploy them manually if required.
The RAT is held in place by an up-lock mechanism inside a storage bay. When it is deployed, the up-lock is released, often by a spring-loaded actuator, allowing the RAT to pivot or move straight out of the bay into the airstream.
The deployment mechanism usually includes linkages and actuators that ensure the RAT is positioned optimally in the airflow, minimising turbulence and maximising performance.
Some designs use struts to extend the RAT further into clean air to avoid disturbed airflow, especially during a crosswind landing.
Published – July 12, 2025 09:54 am IST