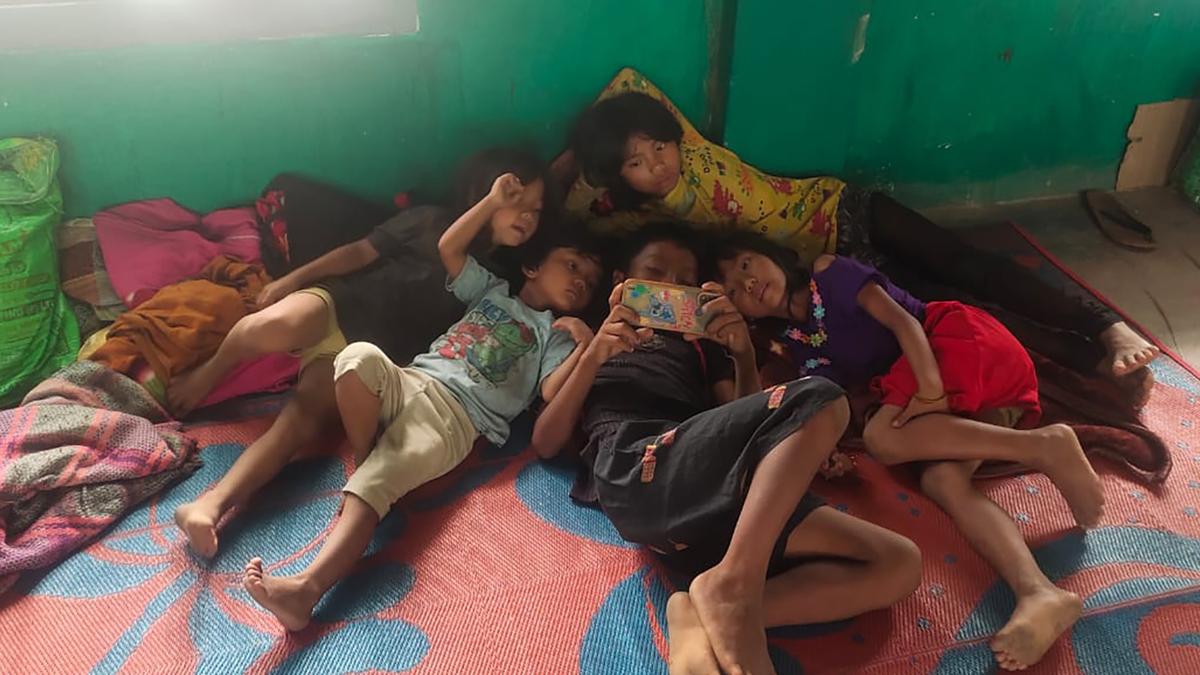
The story so far: Mizoram has been grappling with a refugee crisis since the February 2021 military coup in Myanmar. After months of lull beyond the State’s borders, some 4,000 refugees crossed over from Myanmar in the first week of July following a fratricidal battle between two rival armed groups. Mizoram is now caught between pushing back the refugees who are ethnically related to the State’s dominant Mizos and letting them stay despite limited resources and a tepid response from the Centre.
What triggered the fresh inflow of people?
Within a week from July 3, some 4,000 from Myanmar’s Chin State crossed into Mizoram’s Champhai district. This was after a fierce gunfight between two anti-junta armed groups, the Chin National Defence Force (CNDF) and the Chinland Defence Force-Hualngoram (CDF-H). The two groups are part of the People’s Defence Force aligned with the pro-democracy National Unity Government of Myanmar, which has seized control of large swathes of the Chin State from the junta over the last few months. They are said to have turned against each other to control areas in the region deemed strategic for trade with India. Indian intelligence officials said the CNDF prevailed over the CDF-H and captured its camps.
While the sounds of gunshots have ceased across the Tiau river, which marks a segment of the 510-km border between the two countries, the refugees have not mustered the courage to return to Khawmawi, the village facing Mizoram’s Zokhawthar. Champhai district authorities recorded 3,980 Myanmar nationals in Zokhawthar, a major border trade village, and Saikhumphai on July 6.

When did Mizoram’s refugee crisis begin?
Present-day Mizoram has been used to Myanmar nationals moving in and out of the State even before the Free Movement Regime (FMR) between the two countries came into existence in 1968, allowing residents along their 1,643-km-long border to travel up to 40 km inside. The limit was reduced to 16 km from the border in 2004, and additional regulations were enforced in 2016.
The Centre announced the suspension of the FMR in February 2024, but there has been no official notification or bilateral agreement in this regard, apart from the Ministry of Home Affairs bringing in a fresh protocol in December 2024 to limit the free movement to 10 km. The regulations had little impact on the ground until the February 2021 military coup in Myanmar drove thousands into Mizoram. The State’s government, civil society groups, and villagers provided food, shelter, and security to the refugees on humanitarian grounds, although the Ministry of Home Affairs asked the northeastern States bordering Myanmar not to let the refugees in.
The refugee crisis deepened when some 2,000 Bawm people sought refuge after fleeing persecution in Bangladesh’s Chittagong Hill Tracts in 2022, and thousands of Kuki-Zo people displaced by the ethnic clash in Manipur crossed over. Mizoram houses more than 40,000 shelter-seekers from Bangladesh, Myanmar and Manipur.

How is the State dealing with the situation?
The dominant Mizo community of Mizoram shares ethnic and familial ties with the Chins of Myanmar, the Bawms of Bangladesh, and the Kuki-Zos of Manipur. All belong to the greater Zo ethnic group. In 2024, Chief Minister Lalduhoma told the Centre that ethnic affiliations and humanitarian reasons prevent his government from pushing the refugees back to where they came from. Influential organisations such as the Young Mizo Association (YMA), church bodies, and resourceful individuals have been contributing in cash and kind to take care of the basic needs of the refugees, Myanmar government officials and politicians among them.
Initially reluctant, the Centre provided ₹8 crore as assistance to provide relief for the refugees. However, some villagers began to feel the pressure of handling waves of refugees. In March, the Farkawn village council in Champhai district issued an order asking all Myanmar refugees to stop trading by March 31 and desist from moving out of their designated camps. Civil society groups issued similar diktats in Melthum, a village in Aizawl district, and Lawngtlai town later.
In a departure from the hospitality extended since 2021, the refugees were threatened with eviction if they did not comply with the order. Almost simultaneously, Aizawl-based activist V.L. Thlamuanpuia wrote to Home Minister Amit Shah, underlining the churning in the State over the refugee issue. He stated that the uncontrolled movement of Myanmar refugees was threatening national security, changing the demography, and draining local resources.

How is the government responding?
India is neither a signatory to the 1951 Refugee Convention nor does it have a specific national law on refugees, and it usually deals with them under laws related to foreigners. The country, however, has a history of hosting refugees from neighbouring countries and often works with the United Nations to determine refugee status. New Delhi has been talking tough on the refugee problem along the India-Myanmar border. Of late, the Mizoram government has been showing signs of feeling the pressure of influx from the civil war-torn Myanmar.
In March, the Chief Minister said the FMR was one of the factors responsible for a rise in smuggling activities in the State. A month later, he said some refugees were taking advantage of the crisis in Myanmar to repeatedly cross the border by violating Indian laws. His government has also prodded the Centre to obtain presidential assent for the Mizoram (Maintenance of Household Registers) Bill, that seeks to identify foreigners in the State.
Published – July 13, 2025 01:45 am IST